The entry barrier for phishing is at an all-time low.
Each year, it becomes easier for wanna-be phishers to create successful campaigns. This is well-known. But now, it’s at its easiest. Anyone can successfully set up and employ a phishing scheme – without knowing any programming, going to the darknet or paying a thing.
The Change
Before phishing kits entered the market, a cybercriminal had to possess the technical knowledge and skills to develop and employ a phishing campaign. By removing the technical barrier to launch a phishing campaign, the increase in phishing attacks rose greatly.
Now, imagine the rise of attacks that can be expected when the entry barrier for cybercriminals disappears completely. Welcome to today. Anyone can successfully set up and employ a phishing scheme—without having any programming experience, going to the darknet or paying a thing.
| Let’s take a quick look at the evolution of phishers. Phishing is not new. In fact, the first instance of phishing dates back to the 80s. And, while the goal has always remained the same, the methods of execution have changed dramatically. Even only 5 years ago, it took someone who had to have some programming or web building experience to successfully create a phishing campaign. As you can see below, the bar for becoming a phisher is now non-existent. 1980s (Computer Scientist) As a graduate student at Cornell University in 1988,Robert Tappan Morris created what would be known as the first phishing worm on the internet – just to give himself an idea of the size of the web. The worm was released from a computer at MIT in 1988 in hopes of suggesting that the creator was a student there. 1990s (Anyone with Specialized Knowledge) Phishing attacks rose as underground communities sharing information on how grew. The first phishing campaigns appeared on AOL. Attackers changed their screen names to appear as if they were AOL administrators. Using these phony screen names, they would “phish” for log-in credentials to continue accessing the AOL for free. 2000s (Anyone who was willing to learn had access to the Dark Net) Wanna-be hackers had access to a community via the dark web that harnessed the knowledge from successful hackers. This decade saw the release of Freenet and Tor. 2010s (Anyone with a Credit Card and access to the Dark Net) Phishing kit readily available on the Dark Web to cybercriminals. The kit enables anyone who downloads it to easily craft convincing emails and redirect sites that closely mimic branding elements of well-known firms and launch a phishing campaign that collects the personal and financial information of unsuspecting targets. 2020s (Anyone) Perception Point finds phishing kits for free outside of the darknet. |
The Free Kit that’s Making the Rounds
We first noticed this kit when it was used to impersonate Netflix in an attempt to steal user credentials. The email was made to look like a typical notification, prompting users to click on a phishing URL.
How it’s Done
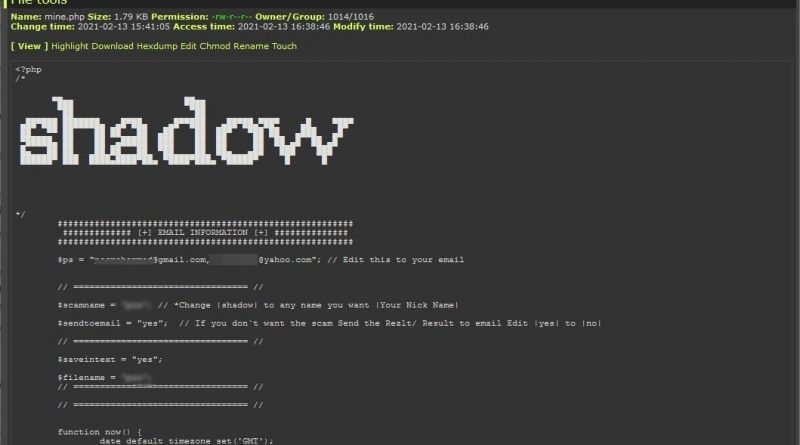
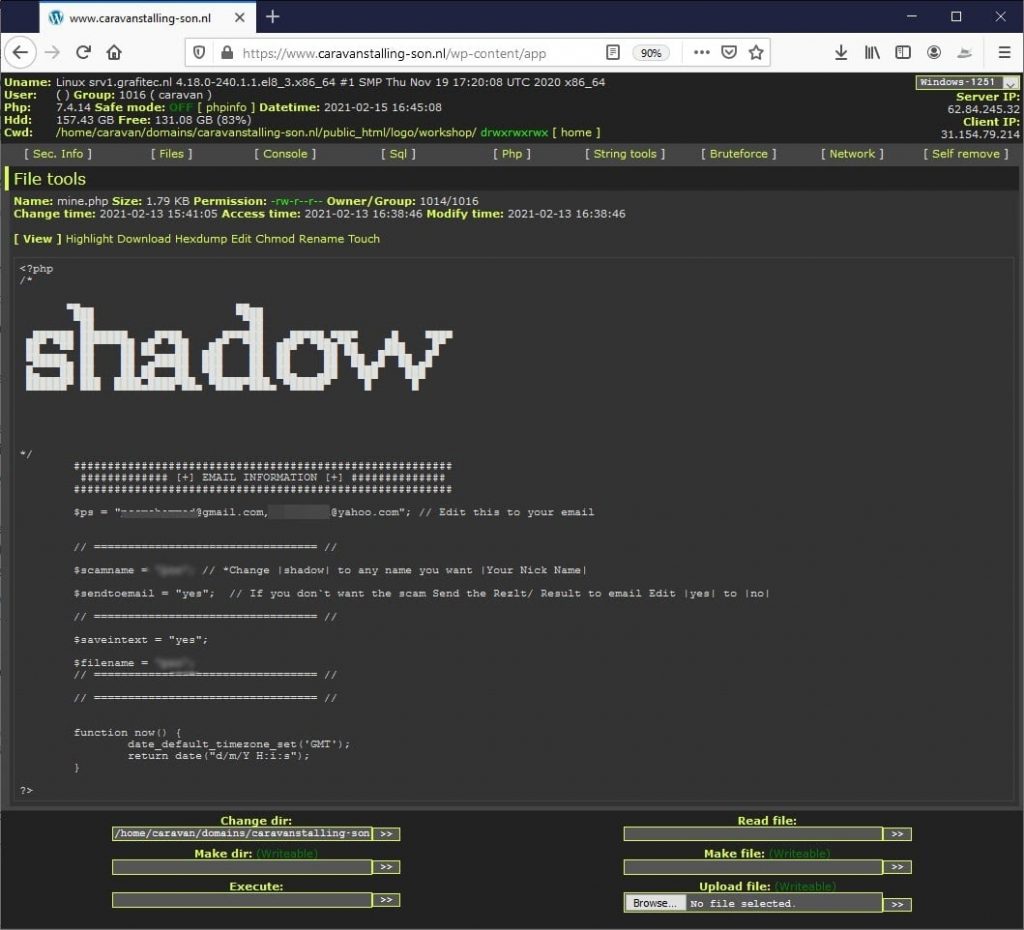
The attacker is using a chain of compromised wordpress sites in order to host its phishing scams. By looking at websites that haven’t disabled XMLRPC, the attacker can use brute force to get access to legitimate wordpress sites. Once he or she has access, then it’s possible to upload a WSO Shell to the site. Webshells are commonly used by hackers to control compromised WordPress sites. It might look simple, but It successfully bypasses Microsoft Office 365 security and stole more than a thousand employee credentials.
Attacker Evasion Method
The attacker changes the IP he or she is sending the email from and uses each compromised wordpress site for a day or two, then switches to the next site. This way he or she is able to remain undetectable for a long time. For example, the campaign mentioned above has been active for more than 3 months now.
About the Phishing Kit
The phishing kit is made up of several php scripts that, when combined, creates the login page, perfectly spoofing the look of an authentic brand.
Netflix email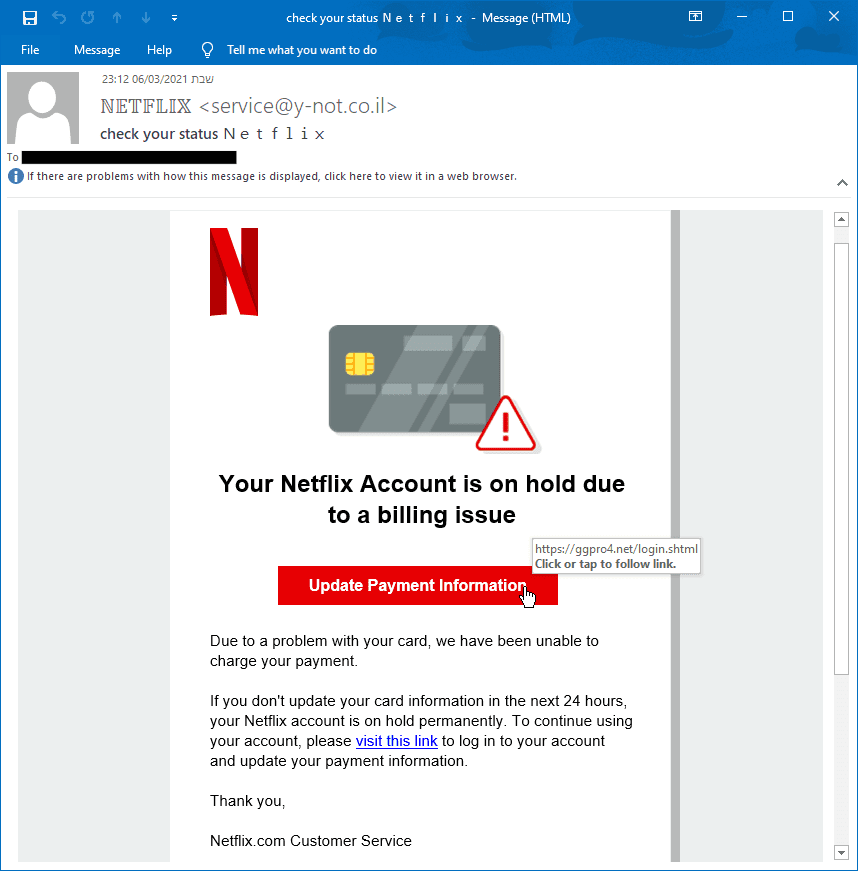 | Netflix login Page | Netflix Payment Page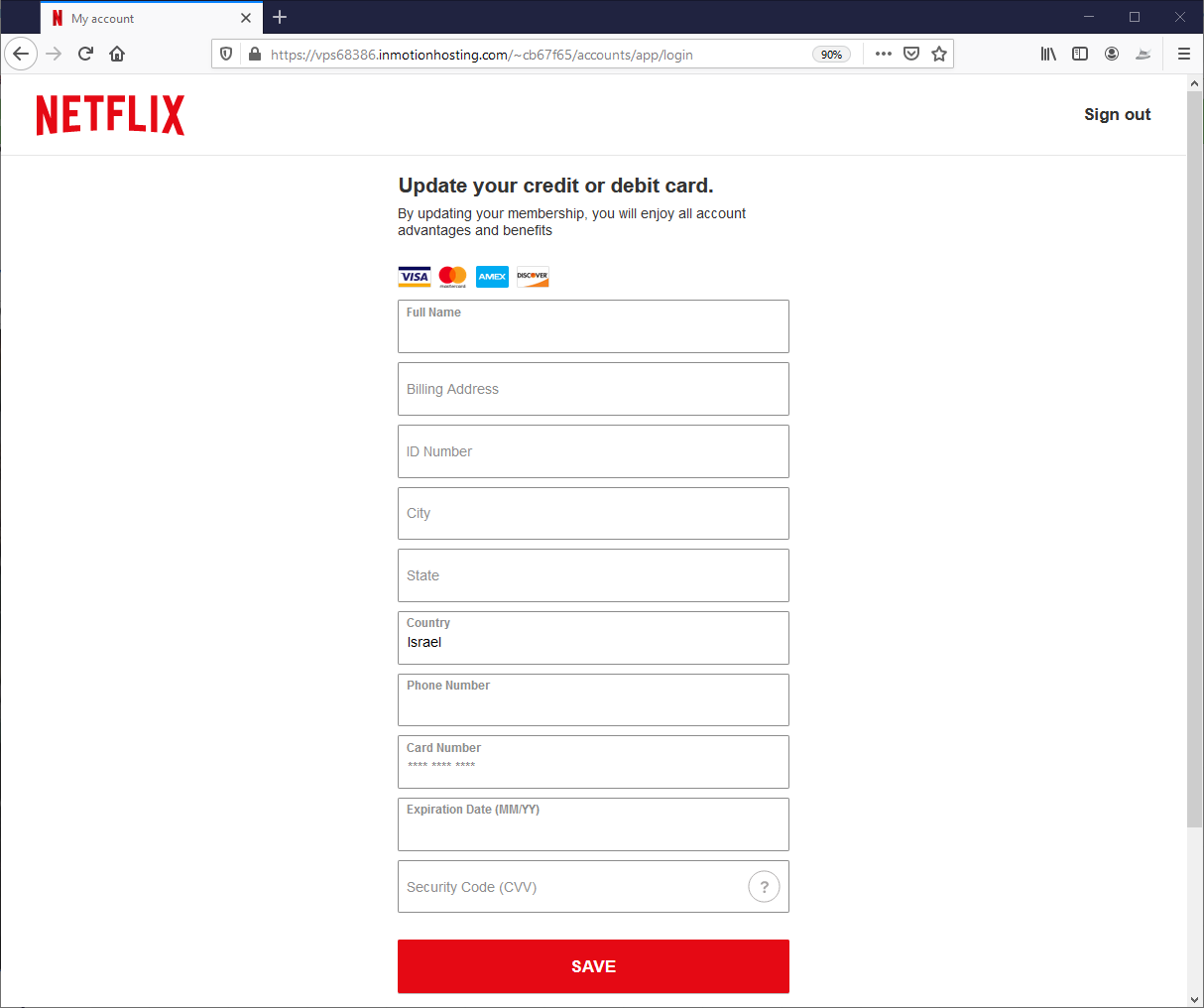 |
One Phishing Kit: Tons of Campaigns
The same kit was also used for another campaign we caught. In those cases, the phishing was done on PayPal brand and Singtel (Singapore telecom).
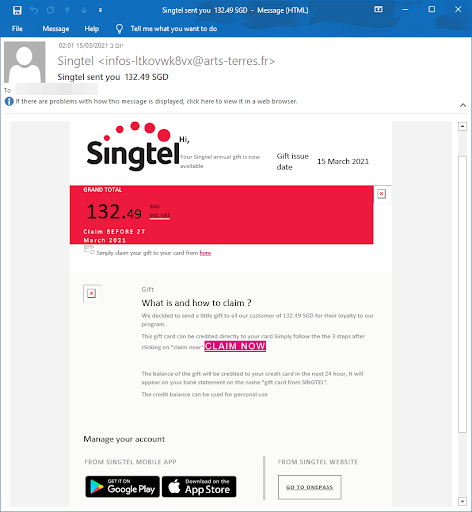 | 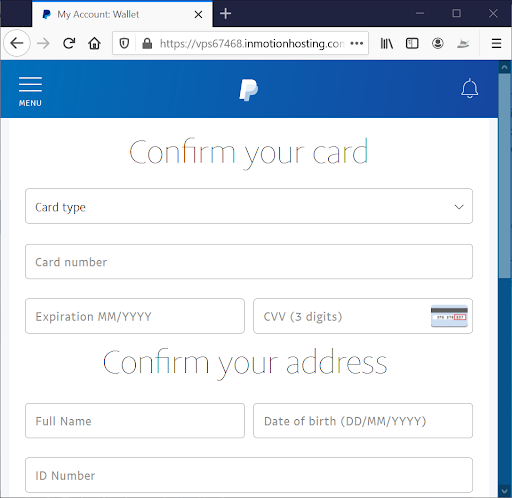 |
Kit Front-End Display
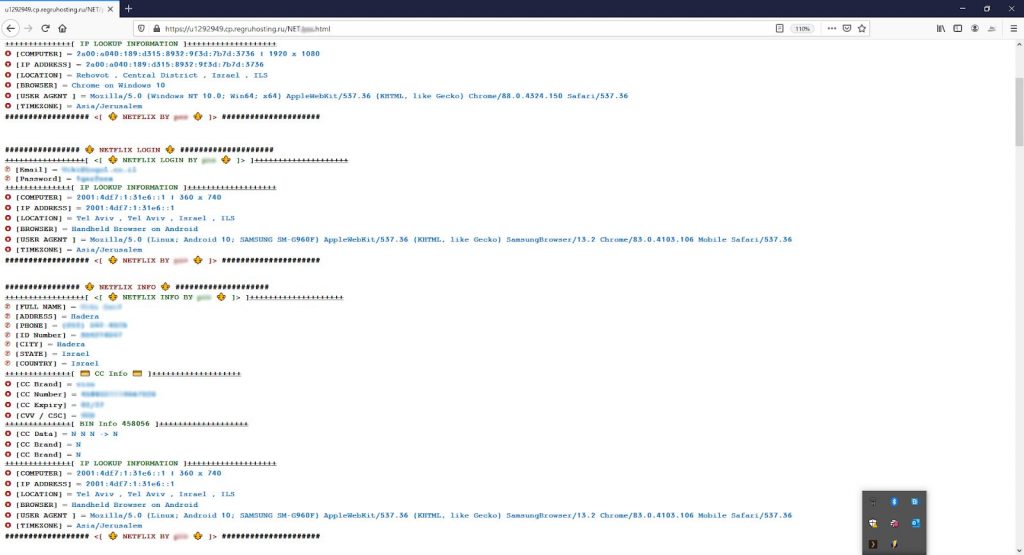
The kit looks very professional, it’s easy to operate, supports multi languages, it has multiple steps and it steals both credentials and credit card info. All that is left to do for the hacker is to put his email address and all the stolen information is sent directly to him.
Kit Evasion Techniques
This KIT is very effective at evading security tools. In most cases, Perception Point detected it after it was already scanned and missed by other security solutions (such as Microsoft ATP).
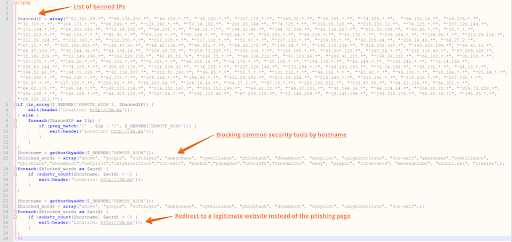
- Malware Spotting. The kit contains a directory called “prevents” with several PHP scripts that all their job is to detect and evade sandboxes and security tools from analyzing the real content of the site.
- Blacklisted IPs. One technique that is used by the hacker is “blacklisted IPs,” basically there is a large databases of IPs that are known to be owned by security firms, so when an incoming request comes from one of those IPs, the KIT will redirect to a legitimate page and not to the fake login page.
- Always Up-to-Date. The kit will always be synced to the legitimate page, so any changes made by the company being spoofed will immediately be updated on the lookalike page. (The ACTIVES folder isn’t part of the original wordpress page, it contains the phishing KIT)
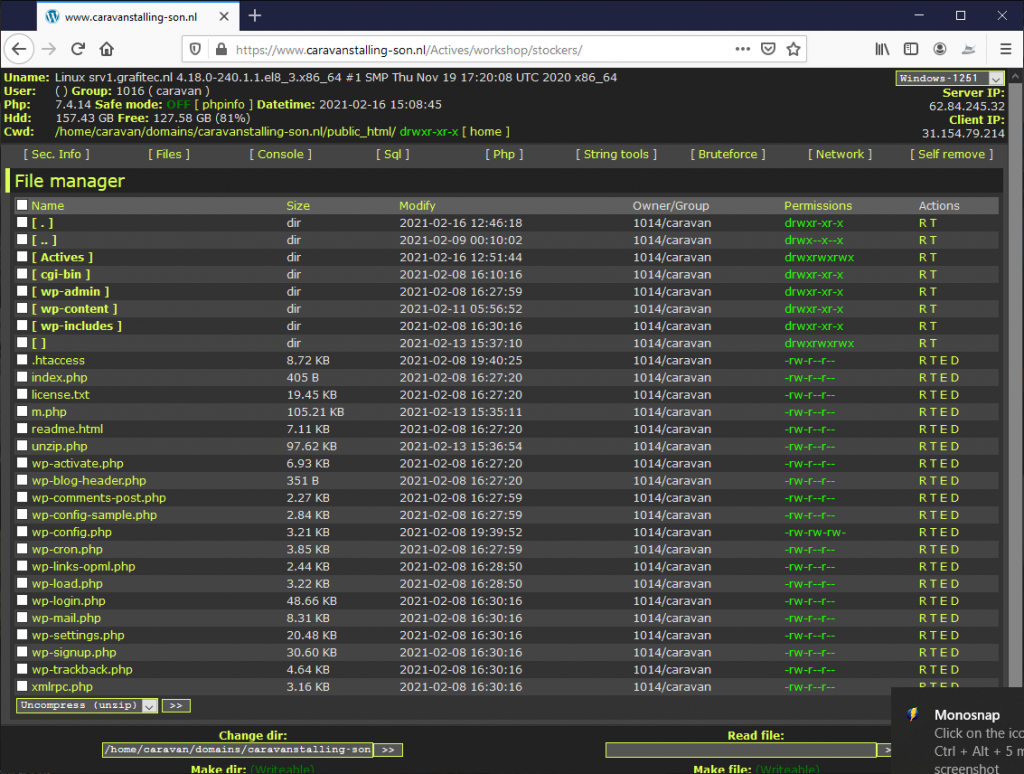
The Payoff: Stealing Credentials
And here is the main page of the kit. You can see how simple the code is. The attacker uses the PHP function “Curl” in order to extract the data from both the login page and the “update credit card” page. The attacker serves it to the user, but redirects the served page so that the submitted passwords are sent to the hacker instead of to Netflix. This way the phishing page looks 100 percent like the real thing.

This following is one of the scripts that’s responsible for evasion. You can see the attacker is blocking all incoming requests coming from known security vendors such as google, phishtank, etc.
As the barrier for phishing attacks has decreased, we can expect a lot more attacks to appear this year, which is why it’s more important than ever that companies protect their email and cloud collaboration channels from advanced threats with additional security layers. Gartner recommends adding a third-party solution to enhance security, as traditional anti-virus and mail scanner solutions still miss a myriad of threats, many of them entering through legitimate email addresses and—increasingly—through cloud collaboration tools and instant messaging platforms.
Dana Roth is the content marketing manager at Perception Point, a security tool for cloud collaboration applications (including email, file-sharing and instant messaging platforms) that catches all threats—before being delivered. Dana has a Bachelor of Journalism from the University of Missouri - Columbia School of Journalism. She loves helping start-up companies achieve their goals (and spending time at the beach!)