Do corporations really care about your security?
“Your security is important to us,” is a common phrase on corporate websites and emails, usually after some data breach that affects customers. To prove that statement, corporations invest billions of dollars in the cybersecurity industry. Most market projections say the industry is worth about $180 billion. About 15 percent of that market goes to data security. But all the indications are that we are losing the war in personal identity security That leaves is with the question: Do corporations really care about customer security?
Probably not
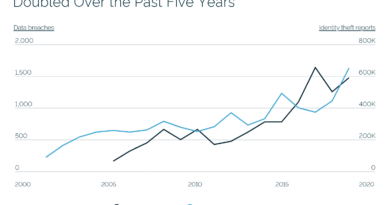
US Department of Health and Human Services reported recently that. in the US, there have been 2,213 breaches since 2020, with 152.1M affected individuals. That is almost half of the American population. But that is just breaches involving medical data.
The FBI reports, in the same period, more than 350 million stolen personal information records, exceeding the known population of the country. Worldwide, the number of personal identity information (PII) records exceeds one billion people.
So how bad is it? “I always tell people assume your social security number has been breached. Just assume that,” said John Meyer, senior director for Cornerstone Advisors, an organization providing security consultation to financial organizations.
So we are spending tens of billions of dollars to protect data from exfiltratation on almost a weekly basis from attacks bypassing current defenses. Is it worth the investment? Does protecting that data even matter?
Well, yes… sort of
Data security professionals say it is and it does. Communications, industry intellectual property, state secrets, and control of crucial systems must still be protected. Most professionals we talked to cite ransomware attacks as the primary reason for investing in security precuts and services.