This is part 1 of our series of articles on OSINT. Find all articles here.
The internet has changed everything around us from education, healthcare, government interactions reaching social communication which receives the greatest impact. The Internet has redefined how people communicate with each other and revolutionized how corporations do business. Nowadays, the majority of world communications happen in what is known as Cyberspace.
According to cybersecurity ventures, by 2030, 90 percent of the human population, aged 6 years and older will be online, this means more than 7.5 billion Internet users. People now use the internet to purchase goods & services, entertainment, connect with other people, share information and files in addition to using social networking websites to communicate with friends and family members without any geographical barriers.
As the world continues to digitalize, digital societies will produce huge amount of digital data generated from people and business interactions in Cyberspace. Exploiting this info in the right direction will open numerous opportunities for public and business organizations to increase profits and operate more efficiently in the new information age.
Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) refers to all information that can be found publicly – mostly via the internet – without breaching any copyright or privacy laws. Under this definition, a wide array of sources can be considered a part of OSINT. For instance, information posted publicly on social media websites, posts on discussion forums and group chats, unprotected websites directories and any piece of information that can be found by searching online. Keep in mind that most OSINT resources cannot be found using regular search engines such as Google or Yahoo!, as many resources are buried deep in the deep and darknet and such resources constitute more than 96% of the web content.
In this article, we will shed the light on the term OSINT, discover its types, actors interested in OSINT gathering and explore OSINT benefits in today’s digital age.
What is OSINT?
As we already mentioned, OSINT refers to all the information which is open for public consumption, this includes both online and offline resources. You may wonder, does this information need to be free to be considered a part of OSINT resources? The answer is No, for example, the information contained in scientific papers, books, and magazine need to be purchased first in order to disseminate it in your OSINT gathering activity.
The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) defines OSINT as follows:
“Open-source intelligence (OSINT) is an intelligence that is produced from publicly available information and is collected, exploited, and disseminated in a timely manner to an appropriate audience for the purpose of addressing a specific intelligence requirement.”
OSINT Types
OSINT can be classified – according to where the public data is found – into the following categories:
- The internet is the main place where OSINT resources are found, indeed, many researchers differentiate between the online OSINT resources and the offline one by using the term “Cyber OSINT” to refer to internet resources exclusively. Internet resources include the following and more: blogs, social media websites, digital files (photo, videos, sound) and their metadata, technical footprinting of websites, webcams, deep web (government records, weather records, vital records, criminal’s records, tax and property records), darknet resources, data leak websites, IP addresses, and anything published online publicly.
- Traditional media channels such as TV, radio, newspapers, and magazines.
- Academic publications such as dissertations, research papers, specialized journals, and books.
- Corporate papers such as company profiles, conference proceedings, annual reports, company news, employee profiles, and résumés.
- Geospatial information such as Online maps, commercial satellite images, geo-location information associated with social media posts, transport (Air, Maritime, Vehicles, and Railway) tracking.
Who needs Open Source Intelligence?
There are different actors interested in OSINT gathering with varying motivation for each one.
Law Firms & Private Investigators
OSINT is used extensively by law firms to optimize their litigation by discovering information found on social media sites and other online places to uncover biases and acquire important information about the individual’s or organization in question. The information acquired from public sources can be beneficial in the following cases:
- Discrimination & sexual harassment lawsuits
- Wrongful termination, disability, and hostile work environment claims
- Intellectual property violation cases
Ethical Hacking
IT security professionals utilize OSINT search techniques and tools to discover weaknesses in friendly IT systems, so such vulnerabilities can be closed before threat actors discover them. Commonly found vulnerabilities include:
- Accidental leaking of sensitive information on social media sites. For example, an unaware employee may post a personal photo in the server room showing the type of security devices used to secure corporate network.
- Open ports and insecure services running can be discovered when scanning the subject network for vulnerabilities using specialized tools.
- Outdated operating system versions, software and any content management systems already in use.
- Leaked information found on data leak repositories or across the darknet.
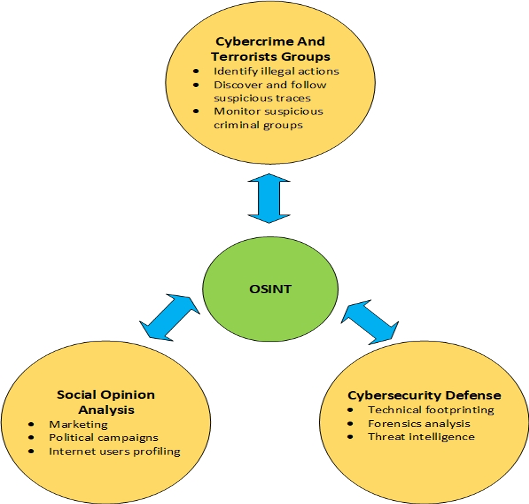
Gain Intelligence About Competitors Activities
As the internet becomes widely adopted in all life and business areas, corporations can utilize OSINT to gain great insight into current and future threats. For example, OSINT can be used to gain useful intelligence about competitors’ marketing and business operations, their deals with other companies in addition to their future plans (e.g. expand to new markets, launch new products or services).
Law Enforcement Agencies
OSINT techniques help Law enforcement officials to improve their intelligence gathering activities to protect citizens and businesses from cybercriminals. OSINT can also utilize in this context to identify possible criminals – by examining their social media accounts and online behavioral – before they commit their crime. For example, law enforcement can use a search algorithm to scan social media sites – and other online public sources sites – for terms like “shoot” or “kill.” to stop possible criminals before conducting any crime.
Government Agencies
Governments are the greatest consumer of OSINT intelligence; they need such info to predict future trends on a global level. Governments seek professional reports concerning any area of interest (political, health, economic or sports events, etc.) from specialized OSINT firms to help them in their decision-making process.
Individuals
Ordinary people use OSINT to check how much personal information is exposed about them online. This helps them to discover and delete any unwanted information leaked publicly and prevent bad actors from exploiting such info to target them with customized attacks (e.g. Social engineering attacks).
In general, all internet users are using some sorts of OSINT search techniques in one way or another, for example, when using Google to search for something, or when using the search box in Facebook or Twitter to search for someone, you are utilizing OSINT to find this info.
Cybercriminals and Terrorist Organizations
In the bad side, cybercriminals and terrorists are using OSINT techniques in the same way good people use to find information about their targets. Threat actors use OSINT to examine possible targets, identify weaknesses in target computer networks and finally use this intelligence to exploit the target.
OSINT is considered a valuable tool to assist in conducting social engineering attacks. The first phase of any penetration testing methodology begins with reconnaissance (in other words, with OSINT).
Conclusion
Pushed by the huge technological advancement and the wide prevalence of internet communication worldwide, OSINT becomes a critical component of both public and private intelligence, supplying businesses, governments, and individuals with a plethora of tools and techniques to gather intelligence from high-quality information to the base and make decisions on. OSINT is beneficial for different scenarios, whether you are conducting an investigation for research, competitor intelligence, vulnerability assessment, threat analysis, or you are simply an individual who cares about his privacy and wants to discover what personal information is already – inadvertently – leaked about him, OSINT will give you the required tools to have access to some of the best available data in the world and mostly for free.
This was an introduction to the OSINT subject, in the next article, we will explore how to implement many OSINT techniques to gather intelligence about our targets using online public sources.
The second part of this series can be found here.
Dr. Khera is a veteran cybersecurity executive with more than two decades worth of experience working with information security technology, models and processes. He is currently the Chief Strategy of ITSEC Group and the Co-founder and CEO of ITSEC (Thailand). ITSEC is an international information security firm offering a wide range of high-quality information security services and solutions with operation in Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Dubai.
Previously the head of cyber security Presales for NOKIA, Dr. Khera has worked with every major telecom provider and government in the APAC region to design and deliver security solutions to a constantly evolving cybersecurity threat landscape.
Dr. Khera holds a Doctor of Information Technology (DIT) from Murdoch University, a Postgraduate Certificate in Network Computing from Monash University and a Certificate of Executive Leadership from Cornell University.
Dr. Khera was one of the first professionals to be awarded the prestigious Asia Pacific Information Security Leadership Awards (ISLA) from ISC2 a world-leading information security certification body under the category of distinguished IT Security Practitioner for APAC.



Pingback: Open Source Intelligence - All you need to know - Cyber Protection Magazine
I would add journalists to your list of those who use OSINT.