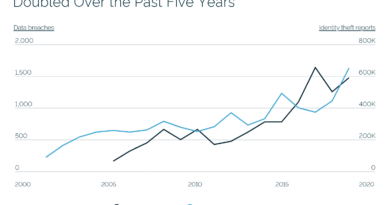
Security concerns reach beyond CISOs
The English riots this past week provide a Dickensian “best of times…worst of times.” context to politics in the United Kingdom and possibly the United States later this year. The UK has had a significant political shift in leadership that brought relief to the majority of that countries citizens (the best) but also encouraged the minority opinion to lash out with provocation from domestic actors and foreign states (the worst). This highlight the fact that digital security concerns reaches far beyond the confines of corporate CISO offices.
The rioters are extreme anti-immigration nationalists whipped up by false information regarding the stabbing of several young children and adults at a dance recital in Southport, a town just north of Wales. The disinformation came from several sources but is primarily coming through a Russian-linked website posing as a legitimate American news organization. The claim was meanwhile amplified up by far-right figures Tommy Robinson and Andrew Tate. Robinson was arrested under anti-terrorism laws but is out on bail has been vacationing in Europe. He is still spreading disinformation. Tate is currently under “judicial supervision” for rape and human trafficking charges. X owner Elon Musk has also participated personally in sewing the discord.
Foreign interference grows
Meanwhile, open source intelligence monitored by companies like Zero Fox and Fletch have identified efforts by North Korea and Russia to interfere in elections of Western countries including Germany and the United States. Zero Fox said, “The Telegram-based bot service IntelFetch had been aggregating compromised credentials linked to the Democratic National Committee (DNC) and their websites. This data, primarily sourced from botnet logs and third-party breaches, includes sensitive information such as login credentials for party members and delegates. This breach poses a significant risk of unauthorized access and potential disruptions to the convention.”
Zero Fox said the DNC had been alerted several weeks ago and that the weaknesses fixed. The DNC Convention is set to begin August 19 and Zero Fox was planning on announcing their findings that day to boost their profile.